Working with Istio on flat network
This document uses an example to demonstrate how to use Istio on Karmada.
Follow this guide to install the Istio control plane on karmada-host (the primary cluster) and configure member1 and member2 (the remote cluster) to use the control plane in karmada-host. All clusters reside on the network1 network, meaning there is direct connectivity between the pods in both clusters.
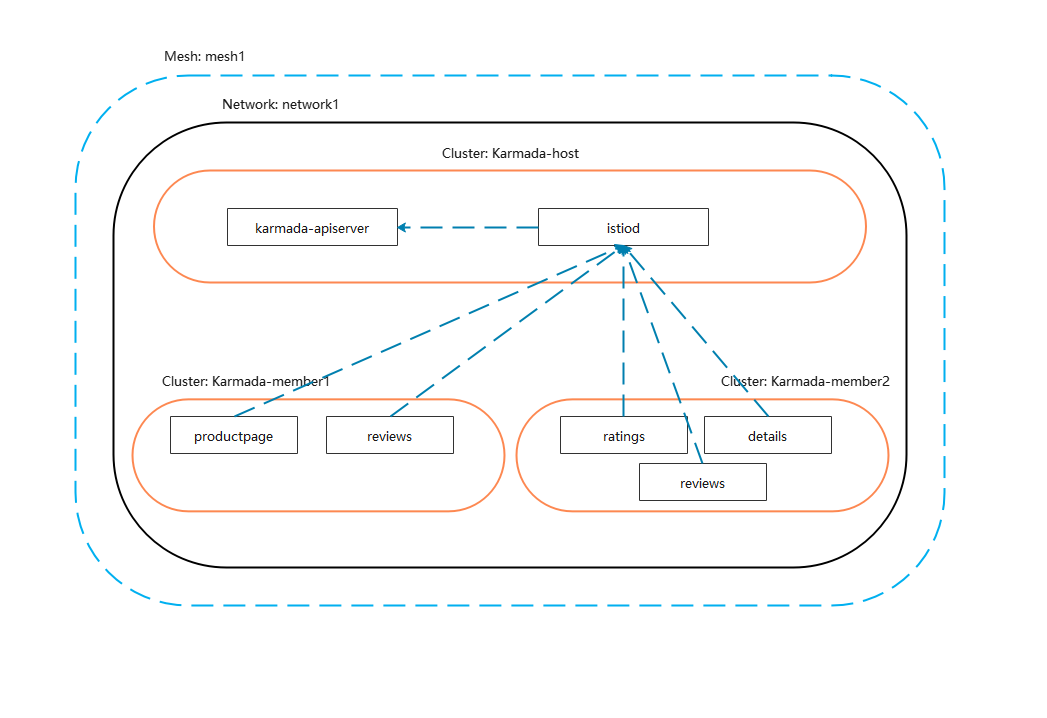
Install Karmada
Install karmada control plane
Following the steps Install karmada control plane in Quick Start, you can get a Karmada.
Deploy Istio
If you are testing multicluster setup on kind you can use MetalLB to make use of EXTERNAL-IP for LoadBalancer services.
Install istioctl
Please refer to the istioctl Installation.
Prepare CA certificates
Following the steps plug-in-certificates-and-key-into-the-cluster to configure Istio CA.
Replace the cluster name cluster1 with primary, the output will looks like as following:
root@karmada-demo istio-on-karmada# tree certs
certs
├── primary
│ ├── ca-cert.pem
│ ├── ca-key.pem
│ ├── cert-chain.pem
│ └── root-cert.pem
├── root-ca.conf
├── root-cert.csr
├── root-cert.pem
├── root-cert.srl
└── root-key.pem
Install Istio on karmada-apiserver
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada apiserver:
# export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/karmada.config
# kubectl config use-context karmada-apiserver
Create a secret cacerts in istio-system namespace:
kubectl create namespace istio-system
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n istio-system \
--from-file=certs/primary/ca-cert.pem \
--from-file=certs/primary/ca-key.pem \
--from-file=certs/primary/root-cert.pem \
--from-file=certs/primary/cert-chain.pem
Create a propagation policy for cacert secret:
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: cacerts-propagation
namespace: istio-system
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
name: cacerts
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member1
- member2
EOF
Run the following command to install istio CRDs on karmada apiserver:
cat <<EOF | istioctl install -y --set profile=minimal -f -
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
meshConfig:
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
values:
global:
meshID: mesh1
multiCluster:
clusterName: primary
network: network1
EOF
Karmada apiserver will not deploy a real istiod pod, you should press ctrl+c to exit installation when Processing resources for Istiod.
✔ Istio core installed
- Processing resources for Istiod.
Install Istio on karmada host
- Create secret on karmada-host
Karmada host is not a member cluster, we need create the cacerts secret for istiod.
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada host:
# export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/karmada.config
# kubectl config use-context karmada-host
Create a secret cacerts in istio-system namespace:
kubectl create namespace istio-system
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n istio-system \
--from-file=certs/primary/ca-cert.pem \
--from-file=certs/primary/ca-key.pem \
--from-file=certs/primary/root-cert.pem \
--from-file=certs/primary/cert-chain.pem
- Create istio-kubeconfig on karmada-host
kubectl get secret -nkarmada-system kubeconfig --template={{.data.kubeconfig}} | base64 -d > kind-karmada.yaml
kubectl create secret generic istio-kubeconfig --from-file=config=kind-karmada.yaml -nistio-system
- Install istio control plane
cat <<EOF | istioctl install -y --set profile=minimal -f -
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
meshConfig:
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
values:
global:
meshID: mesh1
multiCluster:
clusterName: primary
network: network1
EOF
- Expose istiod service
Run the following command to create a service for the istiod service:
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: istiod-elb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
ports:
- name: https-dns
port: 15012
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15012
selector:
app: istiod
istio: pilot
sessionAffinity: None
type: LoadBalancer
EOF
Export DISCOVERY_ADDRESS:
export DISCOVERY_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get svc istiod-elb -nistio-system -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
# verify
echo $DISCOVERY_ADDRESS
Prepare member1 cluster secret
- Export
KUBECONFIGand switch tokarmada member1:
export KUBECONFIG="$HOME/.kube/members.config"
kubectl config use-context member1
- Create istio remote secret for member1:
istioctl create-remote-secret --name=member1 > istio-remote-secret-member1.yaml
Prepare member2 cluster secret
- Export
KUBECONFIGand switch tokarmada member2:
export KUBECONFIG="$HOME/.kube/members.config"
kubectl config use-context member2
- Create istio remote secret for member1:
istioctl create-remote-secret --name=member2 > istio-remote-secret-member2.yaml
Apply istio remote secret
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada apiserver:
# export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/karmada.config
# kubectl config use-context karmada-apiserver
Apply istio remote secret:
kubectl apply -f istio-remote-secret-member1.yaml
kubectl apply -f istio-remote-secret-member2.yaml
Install istio remote
- Install istio remote member1
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada member1:
export KUBECONFIG="$HOME/.kube/members.config"
kubectl config use-context member1
cat <<EOF | istioctl install -y -f -
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
values:
global:
meshID: mesh1
multiCluster:
clusterName: member1
network: network1
remotePilotAddress: ${DISCOVERY_ADDRESS}
EOF
- Install istio remote member2
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada member2:
export KUBECONFIG="$HOME/.kube/members.config"
kubectl config use-context member2
cat <<EOF | istioctl install -y -f -
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
values:
global:
meshID: mesh1
multiCluster:
clusterName: member2
network: network1
remotePilotAddress: ${DISCOVERY_ADDRESS}
EOF
Deploy bookinfo application
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada apiserver:
# export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/karmada.config
# kubectl config use-context karmada-apiserver
Create an istio-demo namespace:
kubectl create namespace istio-demo
Label the namespace that will host the application with istio-injection=enabled:
kubectl label namespace istio-demo istio-injection=enabled
Deploy your application using the kubectl command:
kubectl apply -nistio-demo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.12/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
Run the following command to create default destination rules for the Bookinfo services:
kubectl apply -nistio-demo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.12/samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
Run the following command to create virtual service for the Bookinfo services:
kubectl apply -nistio-demo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.12/samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
Run the following command to create propagation policy for the Bookinfo services:
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -nistio-demo -f -
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: service-propagation
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: productpage
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: details
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: reviews
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: ratings
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member1
- member2
---
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: produtpage-propagation
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: productpage-v1
- apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
name: bookinfo-productpage
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member1
---
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: details-propagation
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: details-v1
- apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
name: bookinfo-details
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member2
---
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: reviews-propagation
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: reviews-v1
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: reviews-v2
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: reviews-v3
- apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
name: bookinfo-reviews
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member1
- member2
---
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: ratings-propagation
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: ratings-v1
- apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
name: bookinfo-ratings
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member2
EOF
Deploy fortio application using the kubectl command:
kubectl apply -nistio-demo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.12/samples/httpbin/sample-client/fortio-deploy.yaml
Run the following command to create propagation policy for the fortio services:
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -nistio-demo -f -
apiVersion: policy.karmada.io/v1alpha1
kind: PropagationPolicy
metadata:
name: fortio-propagation
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: fortio
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: fortio-deploy
placement:
clusterAffinity:
clusterNames:
- member1
- member2
EOF
Export KUBECONFIG and switch to karmada member1:
export KUBECONFIG="$HOME/.kube/members.config"
kubectl config use-context member1
Run the following command to verify productpage application installation:
export FORTIO_POD=`kubectl get po -nistio-demo | grep fortio | awk '{print $1}'`
kubectl exec -it ${FORTIO_POD} -nistio-demo -- fortio load -t 3s productpage:9080/productpage
What's next
Following the guide to confirm the app is accessible from outside the cluster.